Rust logging ⛔
💬 A couple of functions to make logging in Rust easier.
Installation 📦
# Cargo.toml
[dependencies]
rust_logging = "1.1.0"
Usage 📝
Initializing
use rust_logging::*;
fn main() {
// With default settings
let default_logger = Logger::new();
// With custom settings
let settings = LoggerOptions {
error_icon: "💥", // the icon for errors
warn_icon: "⚠️", // the icon for warnings
info_icon: "ℹ️", // the icon for info
success_icon: "✅", // the icon for success
icon_connector: "=>", // the connector between the icon and the message
log_file: "log.txt", // the file to log to when logging to a file
highlight: true, // highlight text after ":" in the message
..Default::default() // the default values for the non specified settings
};
let custom_logger = settings.get_logger();
}
Logging
This code provides the following functions:
- 🟡 warn(): Prints a warning message.
- 🔴 error(): Prints an error message.
- 🔵 info(): Prints an information message.
- 🟢 success(): Prints a success message.
- ℹ️ Add a
fbefore the function name to print the message to the log file
Each function takes a single parameter, which is the message to be printed.
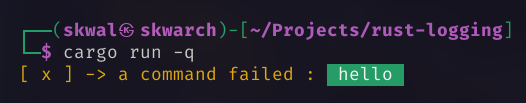
logger.error("a command failed : hello");
logger.info("executing command : hello");
logger.warn("a command is about to fail : hello");
logger.success("a command succeeded : hello");
Highlighting 🔍
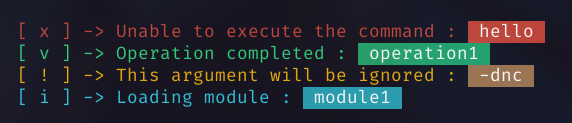
By default, the text after the colon is highlighted.

This can be disabled by setting the highlight field to false inside the custom settings.
let settings = LoggerOptions {
highlight: false,
..Default::default()
};
let logger = settings.get_logger();
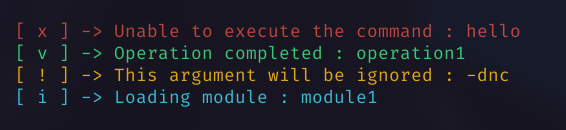
Icon connector 🔗
By default, the icon and the message are separated by an arrow ->

You can change this by setting the icon_connector field to something else.
let settings = LoggerOptions {
icon_connector: "=>",
..Default::default()
}
let logger = settings.get_logger();

Icons 🔍
By default, the following icons are used:
| Icon | Function |
|---|---|
| [ x ] | error() |
| [ i ] | info() |
| [ v ] | success() |
| [ ! ] | warn() |
You can change this by setting the following fields inside the custom settings:
let settings = LoggerOptions {
error_icon: "💥",
warn_icon: "⚠️",
info_icon: "ℹ️",
success_icon: "✅",
..Default::default()
};
let logger = settings.get_logger();
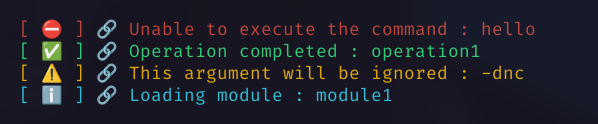
Custom Colors 🎨
You can change the colors of the messages by setting the colors field inside the custom settings.
The value must be a rust_logging::Colors struct.
let my_colors = Colors {
// \x1b is the escape character (ASCII 27) and [xxm is the color 'code'
red: "\x1b[93m", // escape sequence for yellow foreground
bg_red: "\x1b[42m", // escape sequence for green background
..Default::default()
};
let settings = LoggerOptions {
colors: my_colors,
..Default::default()
};
let logger = settings.get_logger();
logger.error("a command failed : hello");
Log file 📄
You can specify the log file path to write the messages to with the log_file field.
Use the f prefix before the function name to print the message to the log file.
let settings = LoggerOptions {
log_file: "myProgram.log",
..Default::default()
}
let logger = settings.get_logger();
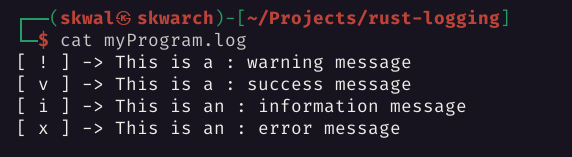
// -----------------------------
logger.fwarning("This is a : warning message");
logger.fsuccess("This is a : success message");
logger.finfo("This is an : information message");
logger.ferror("This is an : error message");
also logging to terminal when logging to file 📄
You can set environment variable LOG to print to also log to the terminal when logging to a file.
LOG=print [program]
#########
# PROGRAM SOURCE CODE #
# ferror("This is an : error message");
#########
[Terminal output] :
[ x ] -> This is an : error message
#########
# LOGFILE CONTENT #
# [ x ] -> This is an : error message
#########
final
If you have any problem, don’t hesitate to open an issue
contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
