Table of Contents📚
Constants
What is a constant❓
A constant is like a variable that can’t be changed.
Declaring a constant
A constant can be declared with the const keyword, followed by the name of the constant, the type, and then the value of the constant. The type of the constant have to be specified.
ℹ️ The constant name is conventionally capitalized, to know that it is a constant.
Example:
const TVA: u8 = 20;
ℹ️ We use the datatype
u8to represent an unsigned 8-bit integer, becauseu8can store values between 0 and 255 and the TVA will always be in this range. It is a good practice to use only the smallest datatype possible, it makes your code more performant.
Using a constant
We can now use the constant in our code. Example, print numbers from 1 to 10:
const MAX_NUMBER: u8 = 10;
fn main() {
for i in 1..MAX_NUMBER {
println!("{}", i);
}
}
ℹ️ Constants have to be declared out of the main function.
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
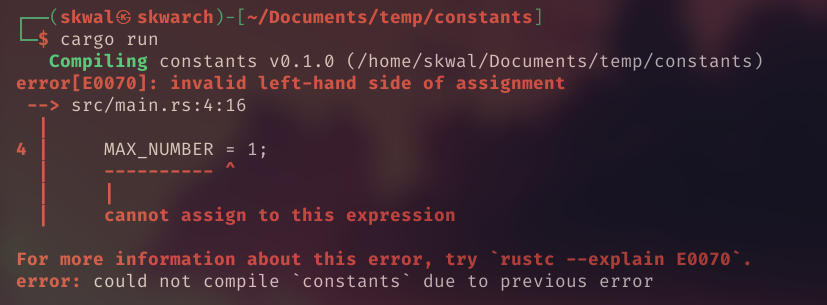
Since we are using a constant, we can’t change its value, if we do, we will get the following error: